Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Primary Colors in the RGB Color Model
- Primary Colors in Different Color Models: RGB vs CMYK vs RYB
- Conclusion
- FAQ
-
- What are the primary colors in the RGB color model?
- Why are red, green, and blue considered primary colors in the RGB color model?
- How does the RGB Color Model work?
- How do the primary colors in the RGB color model relate to human vision?
- How is additive color mixing applied in the RGB color model?
- In what applications is the RGB color model commonly used?
Introduction
In color theory, primary colors are the foundation of all other colors. Understanding the concept of primary colors within the RGB color model is essential for those engaged in digital design, photography, or any visual medium.
This comprehensive guide explores the fundamental principles of primary colors, the RGB color model, and the additive color system. Whether you're a beginner seeking foundational knowledge or an expert in need of a quick refresher, this ultimate guide has you covered.
Primary Colors in the RGB Color Model
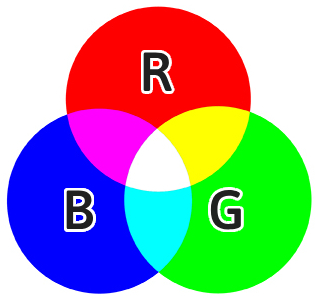
RGB, an additive color model, is the most widely used color model for electronic displays, including televisions, computer monitors, and mobile devices. The primary colors in RGB consist of red, green, and blue. These three colors are considered the building blocks of all other colors in the model. When mixed in different intensities, they can create a wide range of hues, shades, and tones.
The selection of red, green, and blue as primary colors in the RGB model is rooted in how our eyes perceive color. Our eyes have three types of color receptors, or cones, that are most sensitive to these three colors. By using red, green, and blue as primary colors, the RGB color model can accurately represent the colors perceived by our eyes.
In RGB, mixing the primary colors involves combining different amounts of red, green, and blue light. For example, to create the color yellow, the red and green channels must be set to maximum intensity, while keeping the blue channel at zero intensity. Adjusting the intensity of each primary color allows the creation of any color within the RGB color model.
Why are red, green, and blue considered primary colors?
In the RGB color model, red, green, and blue are considered primary colors because they cannot be created by mixing other colors. These three colors are the foundational elements for creating all other colors within the RGB color space:
- Red is associated with warmth, energy, and passion. It is often used to evoke strong emotions and capture attention.
- Green is associated with nature, growth, and harmony. It is commonly used to represent freshness and environmental themes.
- Blue is associated with calmness, stability, and trust. It is frequently used to create a sense of tranquility and reliability.
By blending different intensities of these primary colors, a vast array of colors can be produced in the RGB color model, providing precise control over the appearance of digital images and displays.
In summary, red, green, and blue are considered primary colors in the RGB color model due to their fundamental role in combining to create all other colors in the digital world.
Mixing primary colors in the RGB Color Model
When it comes to mixing primary colors in the RGB Color Model, a diverse palette is achievable by varying the amounts of red, green, and blue. Adjusting the intensity of each primary color allows for the creation of various shades and hues.
One approach to mixing primary colors involves additive color mixing. In this method, starting with black and gradually adding red, green, and blue light creates different colors. For instance, an equal mix of red and green light yields yellow, while combining red and blue light results in magenta.
It's important to note that the RGB Color Model is primarily used for electronic displays and digital imaging, where light is emitted or transmitted. Understanding how to mix primary colors in this model allows us to create vibrant and visually appealing digital content.
Primary Colors in Different Color Models: RGB vs CMYK vs RYB
Understanding primary colors extends beyond the RGB color model, as other color models also have primary colors, each with its own unique characteristics. Let's briefly explore how primary colors operate in RGB compared to other color models, particularly CMYK and RYB, shedding light on their unique characteristics and applications.
RGB vs CMYK
The RGB and CMYK color models serve distinct purposes in the world of color representation. While RGB dominates electronic displays, CMYK takes the lead in printing. Some key differences between RGB and CMYK include:
- RGB, with its additive color system and primary colors red, green, and blue, is ideal for electronic displays where colors are emitted as light;
- CMYK, with its subtractive color system, uses cyan, magenta, yellow, and black as primary colors and is best suited for printing, such as magazines and posters.
RGB vs RYB
The RGB and RYB color models also serve distinct purposes in the world of color representation. While RGB dominates electronic displays, RYB is used in traditional art and painting. Some key differences between RGB and RYB include:
- RGB, with its additive color system and primary colors red, green, and blue, is ideal for electronic displays where colors are emitted as light;
- RYB, with its subtractive color system, uses red, yellow, and blue as primary colors and is best suited for traditional art and painting.
Examples of mixing primary colors in different color models
As noted, different color models have different primary colors and mixing methods. Let's take a look at some examples of mixing primary colors in different color models:
| Color Model | Primary Colors | Mode | Mixing |
|---|---|---|---|
| RGB | Red, Green, Blue | Additive | Red + Green = Yellow Red + Blue = Magenta Green + Blue = Cyan |
| CMYK | Cyan, Magenta, Yellow | Subtractive | Cyan + Magenta = Blue Magenta + Yellow = Red Cyan + Yellow = Green |
| RYB | Red, Yellow, Blue | Subtractive | Red + Yellow = Orange Yellow + Blue = Green Red + Blue = Purple |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the RGB color model's primary colors - red, green, and blue - stand as the bedrock of digital design, offering a versatile palette through additive color mixing. Their selection aligns with the human eye's sensitivity, providing precise control in creating a spectrum of colors. Beyond RGB, this guide highlights the distinctions between color models, emphasizing the essential role of primary colors in diverse creative applications, from electronic displays to traditional art. Mastery of primary colors, especially in the RGB model, remains paramount for those navigating the dynamic landscape of visual expression in the digital age.
FAQ
- 1. What are the primary colors in the RGB color model?
The primary colors in the RGB color model are red, green, and blue. These three colors are considered the building blocks of all other colors in the RGB model. - 2. Why are red, green, and blue considered primary colors in the RGB color model?
Red, green, and blue are considered primary colors in the RGB color model because they cannot be created by mixing other colors. - 3. How does the RGB Color Model work?
In the RGB Color Model, colors are created through additive color mixing. The model utilizes three primary colors: red, green, and blue. These colors are combined in various intensities of light to produce a wide spectrum of colors. When all three primary colors are combined at maximum intensity, they create white light. Adjusting the intensity of each primary color allows for the creation of different colors, providing precise control over the appearance of digital images and displays. - 4. How do the primary colors in the RGB color model relate to human vision?
The selection of red, green, and blue as primary colors in the RGB model is based on the sensitivity of the human eyes. The human eyes have three types of color receptors that are most responsive to these colors, allowing the RGB model to accurately represent colors perceived by our eyes. - 5. How is additive color mixing applied in the RGB color model?
In the RGB color model, additive color mixing is applied by combining different intensities of red, green, and blue light. This process allows for the creation of a diverse palette, with the primary colors serving as the foundation for generating a wide range of other colors. - 6. In what applications is the RGB color model commonly used?
The RGB color model is commonly used in electronic displays, such as monitors, TVs, digital cameras, and other digital applications.
